[ Pacific Security Network News ]
Material:Optical glass N-BK7 , H-K9L, UV Fused Silica, Sapphire, and infrared crystal materials.
Diameter:20-350mm
Diameter Tolerance:+/-0.1mm
Thickness:>2mm
Thickness Tolerance±0.2~0.1mm
Center Deviation:3-5'
Surface quality:80/50 60/40
Coating: Antireflection Coating inside
Chamfers:0.2 x 45° typical
Micro-Single-Single Difference 1: Difference in metering method
The TTL internal metering system in the SLR is to install a dedicated metering sensor at the rear of the pentaprism to calculate the amount of light received by the camera's main sensor, so that the user can use the metering system's reading as a reference. Adjust the parameters of the exposure. So in the optical viewfinder (or shoulder screen and main display) of the digital SLR camera, there is always an exposure reference reading below the image. This reading changes in real time according to the different brightness of the incoming lens image. Users who love to experience the fun of manually manipulating the camera are Use the light meter as a reference to determine the correct settings for the exposure to ensure that it is not overexposed or underexposed.
For micro-single and ordinary portable digital cameras, the metering process does not become a separate system, and there is no complicated photometric sensor device like SLR. The photometry process is completely completed by the main photosensitive element of the camera and the image processor. Without the structure of the reflector, the light directly illuminates the photosensitive element, and the photosensitive element converts the optical signal into an image signal for real-time output to the screen and the image processor. These image signals are analyzed by the image processor and the correct exposure settings are finally obtained.
Micro single SLR difference two: the difference of the auto focus system
The complexity of the internal structure of the SLR digital camera has completely continued from the older generation of film SLRs, so various systems have been retained. In an era when electromagnetics are still underdeveloped, most cameras can only be done in an analog or mechanical manner. The SLR phase difference focusing system is another system independent of framing, imaging and metering.
Phase difference focusing is to achieve focus of the picture by ranging. The component that completes the ranging process is called an AF sensor (AutoFocus). After the SLR camera reflector, there is also a sub-reflector (or sub-mirror), which will send part of the incident light to the AF sensor, determine the focus by ranging, and then control the movement of the lens by the system. auto focus.
Micro-single uses contrast-type focusing, which is not a single focus. Most portable digital cameras and mobile phones, including the iPhone, use this type of autofocus. Like the micro-single metering system, the micro-single focusing system is not a separate system. Contrast focus is still performed jointly by the camera's primary sensor and image processor.
Since the micro-single and the portable digital camera have no reflector structure, the photosensitive element directly receives the external light signal, and the photosensitive element continuously converts the optical signal source into an electronic image signal and transmits it to the image processor. During autofocus and lens movement, the image sensor samples and analyzes the pixels at the user's selected focus, and compares the highest brightness pixel of the position with the brightness value of the lowest brightness pixel. When the difference between the two is the largest, it is considered Focusing is successful.
Micro-Single-Single Difference 3: Differences between Advantages and Disadvantages
Micro-single is a camera device originally created for the high-end consumer and home market. It can be considered as a compromise between portable digital cameras and SLRs. The internal structure is not as complicated as SLR, and the configuration is not as sophisticated as SLR, but compared to home portable digital The camera has the advantage of an interchangeable lens.
But in terms of technology, we still need to see the gap between micro-single and SLR, and the technical complementarity between the two. For example, although electronic technology is developing faster and faster, integration, including focusing, metering, framing, imaging, etc., is a system of micro-single, and the actual speed in focusing, metering, etc. is still more than the SLR subsystem force. There is no catch. Therefore, in some cases, the micro-single is still trying to learn some of the technology of the SLR. For example, Fuji and Sony integrated the AF sensor for phase-difference focusing onto the main photosensitive element, so that the micro-single has the high efficiency of phase-difference focusing.
On the other hand, the portability of the micro-single phase compared to the SLR has also become a constraint for the micro-single to expand its own positioning. The micro-single is limited by the user's portability requirements, and the camera's flange distance is relatively small, which not only brings design difficulties, but also causes edge dispersion and vignetting problems in imaging. fixed.
We are manufacturing high transmission and durability domes. BK7 or HK9L Glass domes are often used in meteorology applications. Fused silica domes are commonly used in underwater applications at extreme environments. Other application for our dome include meteorology applications, pyranometers, defence applications and as high pressure view ports in underwater cameras and submersibles.
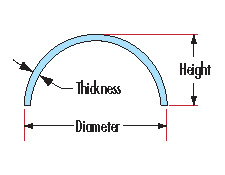
Material:Optical glass N-BK7 , H-K9L, UV Fused Silica, Sapphire, and infrared crystal materials.
Diameter:20-350mm
Diameter Tolerance:+/-0.1mm
Thickness:>2mm
Thickness Tolerance±0.2~0.1mm
Center Deviation:3-5'
Surface quality:80/50 60/40
Coating: Antireflection Coating inside
Chamfers:0.2 x 45° typical
Hemisphere Dome Lens,Hemispheric Glass Domes Lens,Optical Glass Hemisphere Domes Lens,120 Mm Diameter Glass Dome Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.csoptlens.com