1. The brightness of the brightness LED is different and the price is different. LEDs for LED luminaires shall comply with the laser class I standard.
2, anti-static ability Anti-static ability of the LED, long life, and therefore high price. LEDs with an antistatic greater than 700V are usually used for LED lighting.
3. LEDs with the same wavelength and wavelength have the same color. If the color is consistent, the price is high. It is difficult for manufacturers without LED spectrophotometers to produce pure color products.
4. Leakage current LED is a unidirectional conductive illuminator. If there is reverse current, it is called leakage, and LED with large leakage current has short life and low price.
5. LEDs with different illumination angles have different illumination angles. Special lighting angle, the price is higher. Such as the full diffusing angle, the price is higher.
6. The key to different quality of life is life, and life is determined by light decay. Low light decay, long life, long life and high price.
7. The illuminator of the wafer LED is a wafer, and the price of the wafer varies greatly. The chips in Japan and the United States are relatively expensive, and the prices of wafers in Taiwan and China are generally lower than those in Japan and the United States.
8. Wafer Size The size of the wafer is indicated by the side length. The quality of the large wafer LED is better than that of the small wafer. The price is proportional to the size of the wafer.
9, colloidal ordinary LED colloid is generally epoxy resin, LED with anti-ultraviolet and fire retardant is more expensive, high-quality outdoor LED lighting should be resistant to UV and fire. Each product will have different designs. Different designs are suitable for different purposes. The reliability design of LED lighting includes: electrical safety, fire safety, environmental safety, mechanical safety, health and safety, and safe use time. From the perspective of electrical safety, it should comply with relevant international and national standards.
Metallographic Microscope Series
The structure of optical metallographic microscope generally includes magnification system, optical path system and mechanical system, among which the magnification system is the key part. The preparation process of metallographic samples generally includes five steps: sampling, rough grinding, fine grinding, polishing and etching. The interception of samples from metallic materials and parts to be tested is called "sampling". Selection of sampling sites and grinding surfaces must be based on analysis requirements. The size of the sample is not uniform, from the perspective of easy to hold and grinding, the general diameter or side length of 15~20mm, 12~18mm high is suitable. For those too small, irregular shape and the need to protect the edge of the sample, you can adopt Mosaic or mechanical clamping method. For the inlay of metallographic sample, the appropriate size (about φ L5-20mm) of steel tube, plastic tube or paper shell tube is placed on the smooth plastic (or glass) plate, and the sample is placed in the tube to be ground face downwards into the filler, which can be solidified and hardened for a period of time. 3) Chamfering On the premise of not affecting the purpose of observation, the edges and corners on the sample should be ground off to avoid scratching the sandpaper and polishing fabric.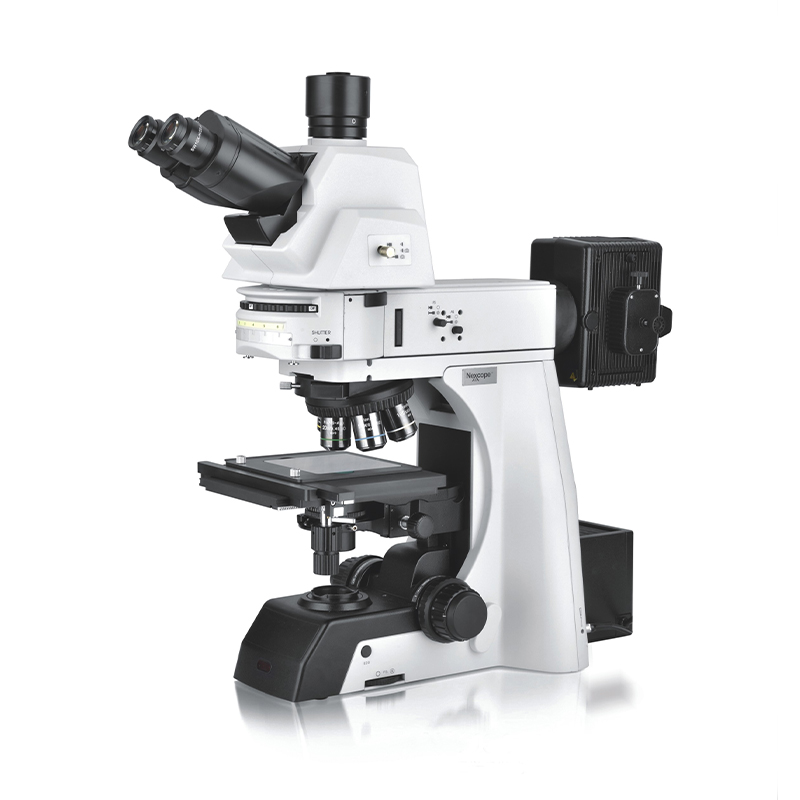
metallurgical analysis,optical microscope for metallurgy,metallurgy microscope
TROJAN (Suzhou) Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.trojanmaterials.com