When two-liquid quenching: How to determine the cooling time in water or brine? How to determine the cooling time in oil?
A: The key to the operation of the dual-medium quenching method is to control the water cooling time of the workpiece. There are three methods for controlling water cooling time:
(1) One is the calculation method:
According to practical experience, when the workpiece size is φ5~φ30mm, the cooling time can be calculated every 2.5~3.3s/10mm. For workpieces with cross-section size larger than φ30mm, it is calculated according to 3.3~6.7s/10mm, which has complex shape and high deformation requirements. The mold is sometimes supercooled, that is, the water cooling time is calculated every 1.25 to 2 s/10 mm. For those with large sections, the upper limit should be taken, and for those with small sections, the lower limit should be taken. In order to control the water cooling time, the quenching is usually controlled by a number of methods. Normal people can only count up to 4 in the fastest ls, so usually the fastest speed when quenching, every 4 to 4 times, the cooling time can be regarded as Ns. The number begins when the workpiece is quenched into the cooling medium.
(2) One is the sensory method:
It is judged according to the severity of the boiling cooling of the workpiece during quenching. When the workpiece is cooled in water and the jitter is small, if it is not strong, it can be turned to oil immediately.
(3) The last method is the auditory method:
When the workpiece is quenched into the water, the humming sound is already weak and it is immediately cooled to the oil when it is stopped.
These three methods are relatively stable by counting and counting methods. If the three methods are combined to control, the control of water cooling time is easier to master.
Determination of cooling time in oil: Calculated according to D (effective thickness of workpiece, mm) × (0.05 ~ 0.10) min / mm.
The shorter the time from water transfer to the oil pool, the better the small parts should be controlled within 2 seconds. Large transfer time is difficult to operate and generally exceeds 2 seconds.
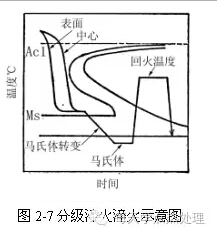
What is graded quenching? How to operate? How to determine the timing of quenching grading?
Answer: Graded quenching: The austenitizing work is quickly quenched into a cooling medium with a temperature slightly higher than Ms. After a little heat preservation, the air is cooled to room temperature to complete the martensite transformation. This quenching method is called classification.
The heating temperature of the staged quenching can be slightly higher than that of the general quenching, mainly to increase the stability of the supercooled austenite. And increase the temperature difference between the quenching temperature and the grading temperature, so as to appropriately increase the cooling rate to ensure that no high temperature transition occurs. The grading temperature is usually chosen to be slightly higher than the temperature of Ms (Ms + 10 ~ 20 ° C), see Figure 2-7 after the end of isothermal, the workpiece is taken out and cooled in air or other slow medium.
Determination of the grading isothermal time: (1) The isothermal time t (min) after entering the isothermal tank should be such that the center and surface of the workpiece reach the isothermal temperature, which can be calculated empirically: t = effective heating dimension of the workpiece (mm) × coefficient a (min / mm), generally a value: 0.05 ~ 0.08.
What is austempering? How to operate? How to determine the time of austempering?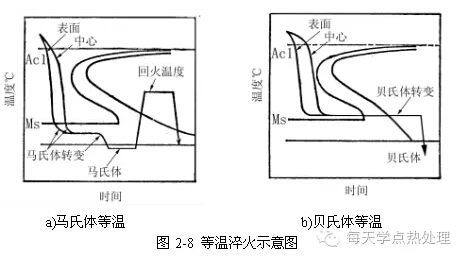
Answer: Austempering: The workpiece after quenching and heating is quickly placed in a hot bath with a temperature higher than the Ms point (Ms ~ 350 °C). The isothermal temperature is longer and the workpiece is fully subjected to lower bainite transformation. This quenching method is called It is austempered (see Figure 2-8).
The method of austempering is similar to the classification. The difference is the difference in isothermal temperature, time and grading.Determination of the isothermal time: (1) The isothermal time t (min) after entering the isothermal bath can be calculated empirically: t = effective heating dimension (mm) of the workpiece × coefficient a (min / mm), generally a value: 0.5 ~ 0.8. (2) According to the isothermal transition time on the isothermal cooling curve, the homogenization time of the workpiece can be ignored.
Special thanks to Teacher Wang Qinghua!
We focused on international export product development, production and sales. We have improved quality control processes of Crystal Roller Shutter Door to ensure each export qualified product.
If you want to know more about the products in Crystal Roller Shutter Door, please click the product details to view parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Crystal Roller Shutter Door.
Whatever you are a group or individual, we will do our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive message about Crystal Roller Shutter Door!
Commercial Rolling Up Door,Roller Shutter Door for Shop,Crystal Roller Shutter Door,Commercial Roller Shutter Doors
Shenzhen Hongfa Automatic Door Co., Ltd. , https://www.pvchighspeeddoor.com