Abstract: The water-cooled tungsten argon arc welding process has successfully achieved the welding of large-section copper busbars. The construction and operation of the plant show that the process overcomes the shortcomings of the traditional “carbon arc welding†process, which is easy to cause welder poisoning, easy to carburize welds, poor plasticity and large electrical resistance. It has stable welding quality, easy operation, safety and construction cost. Lower advantages.
The connection of the copper busbar is often encountered in power stations and metallurgical installations, and the connection method is a clamping method (stud fastening), a welding method, and the like. For the welding of large-section copper busbars, the current domestic data show that there are several kinds of carbon arc welding, submerged arc welding and tungsten argon arc welding. The preheating temperature of carbon arc welding is relatively high, and the temperature of the base metal of the weld must be above 750 °C. The appearance of the weld is generally formed, and the Cu2O vapor generated at high temperature is easy to poison the welder, and it is easy to cause carburization, plasticity is poor, and the electrical resistivity is relatively high. Big. Submerged arc welding preheating temperature is slightly lower, about 500 °C, the quality is relatively stable, but the current and voltage are slightly higher, respectively 750 A ~ 800 A, 40 V ~ 50 V, and the amount of flux is large, there is no welding in China Introduction of large section and large length busbars. Tungsten argon arc welding from the current domestic specifications shows that it is only suitable for copper busbar welding with δ<12, and the copper busbar welding of single-sided V-groove with δ>12 is not instructive.
In the two sets of 15 000 tons / year electrolytic zinc plant in Shangluo zinc smelting plant, the design requires the use of welded joint method, but the welding process and method are not clear. On the basis of fully considering the improvement of weld quality and labor environment, we draw on domestic and foreign experience and adopt the water-cooled tungsten argon arc welding process under preheating conditions. The weld appearance is well formed and the internal quality assurance is qualified. The basic solution to the slag inclusions and porosity defects commonly found in copper welding has successfully completed the installation tasks of the project.
1 Solderability of copper
The copper used in the project is oxygen-containing copper T1, and its total impurity content is 0.05, wherein oxygen is 0.02, and its physical properties are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Physical properties of oxygen-containing copper T1
Index index value index index value lattice type face-centered cubic lattice thermal conductivity 386.4W / (m · k)
Melting point 1083 ° C Linear expansion coefficient 16.5 × 10-6 K-1
Boiling point 2580 ° C resistivity 168 × 10-10 Ω · m
Density 8.96kg/cm3
The thermal conductivity of copper is 7 times larger than that of iron at 20 °C and 11 times larger at 1 000 °C. The heat is quickly conducted from the heating zone during welding, making it difficult to fuse the base metal with the filler metal. Therefore, a high-power heat source must be used for welding. Preheating is adopted, and the molten pool is formed easily during welding.
The coefficient of linear expansion of T1 is 15% larger than that of iron. In order to avoid the occurrence of attack in the near seam area and to ensure the gap during welding, sufficient clearance should be ensured when the pair is in pairs; at the same time, the shrinkage rate is more than 1 times larger than that of iron, to prevent the weld pool. When the liquid phase changes to a solid state, the temperature difference between the layers is large to form a pattern, so the interlayer temperature should be ensured during the welding.
When oxygen-containing copper is welded, it is easy to form pores. The main causes are oxygen and water vapor. Among them, oxygen forms reaction pores, and water vapor generates diffusion pores. Therefore, measures such as deoxidation and slow cooling of the solder powder must be taken.
In order to prevent the occurrence of lead-rich or rich low-melting eutectic, the water should be quickly cold-cut after welding, and the hammer should be reduced.
In order to ensure smooth joints and reduce heat loss at the root of the weld and to reduce heat loss, graphite pads, baffles and blockers should be prepared during welding.
2 Preparation before welding
2.1 Preparation of tools
1) Make a coke heating furnace.
2) Prepare a graphite backing plate.
3) Prepare 2 pieces of graphite baffle and blocker.
4) Asbestos is used as insulation material.
2.2 Group pair and preheating
1) The groove is machined by planer, which is single-sided V-shaped, with 55°±5° groove angle and 1 mm blunt edge. The pre-heating group should have a gap of 4 mm to 5 mm.
2) Before the group is paired, use a sander to treat the protective layer within 50 mm of the groove side until the metallic luster is exposed.
3) Preheating is shown in Figure 1.
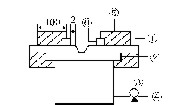
Figure 1 Preheating device
 1-busbar; 2-graphite pad; 3-coke furnace;
 4- blower; 5- asbestos; 6-baffle
3 welding process
3.1 Selection of welding machine and welding consumables
1) The welding machine is equipped with 2 sets of Z630 welding machines, which are connected in parallel and positively connected to ensure smooth current. The welding torch is 500 A.
2) The welding wire is made of Φ6 copper welding wire, and sanding is used before welding, and the flux is selected from the air agent 301.
3.2 Preheating
After the preheating is continued to be heated to 350 ° C ~ 600 ° C in a coke oven (take the far infrared thermometer test), after the asbestos is wrapped on both sides of the weld 400 mm wide, turn off the blower to ensure that the furnace continues to heat. At this time, the pair of gaps are contracted by the expansion to 2 mm to 3 mm, and the gas agent 301 is evenly sprinkled in the weld zone, and then the welding can be performed.
3.3 Welding process parameters
The welding process parameters are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Welding process parameters
Welding layer number current voltage tungsten wire argon flow rate bottoming 350 A 20 V Φ6 铈 tungsten electrode Φ6 15~17 (L/min)
Filling cover 400 A 20 V Φ6 铈 tungsten Φ6 15~17 (L/min)
When welding, the left welding method is adopted, and in order to reduce oxidation, the welding speed should be fast. In order to facilitate the observation of the molten pool and the filling of the welding wire, the angle between the welding torch and the workpiece should be 75 ° C ~ 85 ° C, the angle between the welding wire and the welding element is 10 ° ~ 20 °, the welding torch should be linearly and forwardly moved evenly and smoothly during operation. And maintain a constant arc length, the arc length is generally controlled at 2 mm ~ 4 mm, when filling or covering the surface, the wire should be slightly laterally pendulum, after the joint is filled, gradually expand the arc arc extinguishing.
When welding between layers, the temperature in the weld zone should be continuously maintained at around 350 °C ~ 600 °C, and it should not be too long.
300×16 copper plate welding, from heating to welding, generally takes about 40 minutes, and the welding time is only 10 minutes.
4 post-weld treatment
1) After welding, the water-cooling method should be used for rapid cold cutting, hammering and reducing, preventing low-melting eutectic and increasing copper busbar toughness.
2) After cooling, clean the slag with a wire brush and pickle and remove the oxide layer in the heat affected zone of the weld.
3) Visual inspection of the weld.
5 equipment equipment
The welding equipment is prepared as follows.
Welder Z630 2 parallel welding guns 500 A water-cooled argon arc welding machine 1 plasma cutting machine Z200 1 air compressor 1 air blower 200ω 1 furnace 400×500 2 graphite plates δ20 20 crossings / 1 crane 8t 1 set Inverted chain 2t 2 infrared temperature measuring gun M130T 1 anti-auxiliary labor insurance clothing 2 sets
6 Labor organization
2 welders, 2 shovel, 1 furnace, 1 plasma cutter, 1 technician, 1 technician
7 Quality standards and inspection
7.1 Quality Standard
The surface quality of the butt joint is performed according to HGJ223-1992, the intrinsic quality is qualified in JB4730-1994 grade II, and the resistivity is measured by the double-arm bridge test, which should comply with GBJ149-1990.
7.2 Quality Assurance Measures
1) Perform the welding procedure assessment and determine the operation instructions after the on-site test welding.
2) The welder can be employed after passing the training.
3) The measuring instruments on the welder and the argon cylinder must be accurate during the calibration period.
4) Strict process handover inspection system, the unqualified part must be processed before proceeding to the next process.
8 Welding quality
Two 300×200 test pieces used in the process test were subjected to X-ray photography after visual inspection, coloring display, and no defects. After testing, no slag inclusion defects, only one stomata, grade II according to JB4730-1994 qualified. Then, the test was carried out and the mechanical properties test was carried out. The test results were in accordance with the requirements of HGJ223-1992. The resistivity was measured by the double-arm bridge test. The maximum resistivity of the test results was 0.015 Ωmm2/m, which met the requirements of GBJ149-1990.
9 Economic Benefit Analysis
After adopting the welding process, the appearance of the weld is well formed, the quality is ensured, the strong auxiliary injection of the carbon arc welding high temperature to the welder is avoided, and the adaptation place is larger, and after heating with a large torch for the place where the furnace heating is difficult, It can also be welded smoothly. At the same time, various types of joints such as busbars and conductive sheets (corner welds) and busbars (butt joints) can be successfully welded under the guidance of them, and the scope of application is wider.
Compared with carbon arc welding, argon arc welding has lower resistivity, less weld porosity and more stable quality. Compared with submerged arc welding, argon arc welding is easier for the welder to master, and is more suitable for narrow width and large length on site. Busbar welding; compared with the original busbar clamp connection, after the argon arc welding, the busbar consumes less power. The first phase of the commercial plant is put into production, which shows that each ton of electrolytic zinc sheet produced is 60 degrees lower than the original one, which can be reduced annually. The cost is about 450,000 yuan, and the economic benefits are obvious.
10 engineering application examples
Shaanxi Zinc Industry Company Shangluo Zinc Plant has more than 80 tons of copper busbars in the 15,000-ton/year electrolytic zinc project. The material is T1, the section is 300 mm×16 mm, 200 mm×12 mm, 200 mm×28 mm. Etc., a single busbar is up to 17 m long, and some conductive sheets (250 mm × 12 mm, spacing 62 mm) are connected to the corners of the busbars and inlaid, and the design requirements are all welded. We use argon arc welding under preheating conditions, and the appearance of the weld is well formed. The test specimens, the intrinsic quality, mechanical properties and electrical resistivity of the joints all meet the design requirements. The welding period of each set is only 25 days. The task was completed ahead of time to ensure the smooth operation of the plant.
11 Conclusion
1) Tungsten argon arc welding is a method for low-profile copper busbars with low preheating temperature, stable welding quality, convenient operation and good welding environment. It has welding of copper and its alloys with δ>12 mm. A certain guiding role. However, the existence of pores in oxygen-containing copper welding is difficult to eliminate by using solder powder to ensure that the interlayer temperature is still eliminated. In theory, the pores can be eliminated by controlling the content of hydrogen and nitrogen in argon and the surrounding environment, but in practice, Hard to reach.
2) The part where the pores are generated is mainly the welded joint, which is caused by the temperature drop after the arc extinguishing and the gas is too late to precipitate. Therefore, it is advisable to pick up long electrodes and continuously weld each layer.
3) For the copper busbar angle connection, soft connection and inlaid connection of different sections, the preheating temperature and process parameters are not much different from the parameters when docking. It is advisable to adopt appropriate preheating method (such as boat welding) according to the section size and joint type. Welding is performed.
Hex Head Hollow Bolts,Hex Steel Flange Bolts,Countersunk Bolts,Flange Bolts
CANGZHOU LINGANG YUANFENG IMPORT & EXPORT TRADING CO.,LTD , https://www.clyfhardware.com